|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
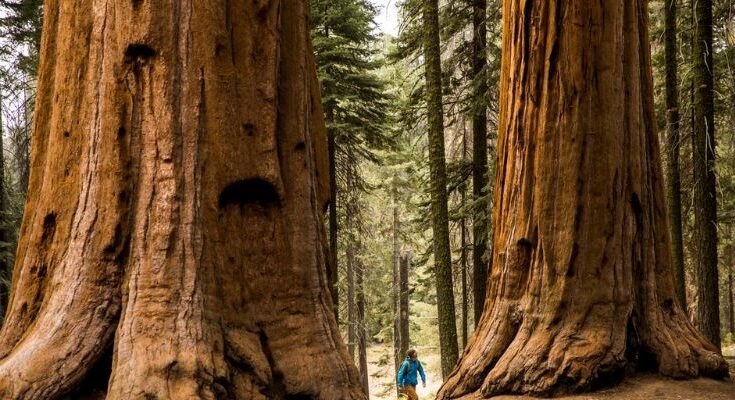
Nestled in the heart of California’s Sierra Nevada mountains, the Giant Sequoia (Sequoiadendron giganteum) stands as one of nature’s most awe-inspiring creations. These colossal trees have fascinated botanists, nature enthusiasts, and travelers for centuries. In this blog post, we delve into the unique characteristics, intriguing facts, and various aspects of the Giant Sequoia that make it a natural wonder worth exploring.
Giant Sequoia Tree Scientific Classification
| Category | Classification |
|---|---|
| Kingdom | Plantae |
| Clade | Tracheophytes |
| Clade | Gymnosperms |
| Order | Pinales |
| Family | Cupressaceae |
| Subfamily | Sequoioideae |
| Genus | Sequoiadendron |
| Species | S. giganteum |
Giant Sequoia Characteristics
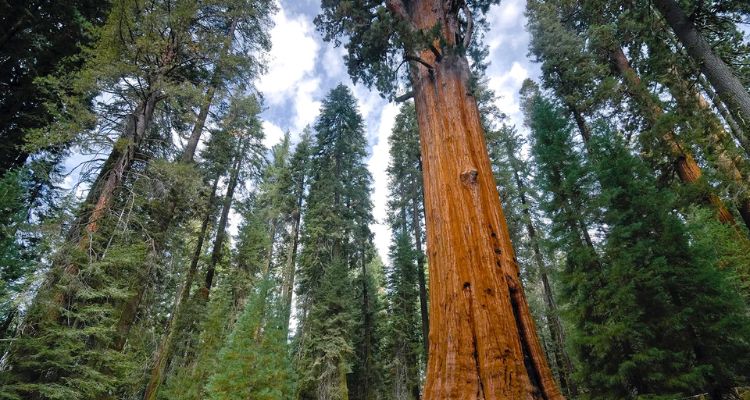

The Giant Sequoia, also known as the Sierra Redwood, is renowned for its immense size and age. These trees can reach astounding heights of 250 to 300 feet, with trunk diameters exceeding 20 feet. Their bark, which can be up to three feet thick, is a reddish-brown hue and deeply furrowed, providing a distinctive, rugged appearance. This thick bark not only adds to their grandeur but also offers significant protection against forest fires and pests.
Giant Sequoias have a conical shape, tapering towards the top, which allows them to withstand heavy snowfalls without breaking. Their root systems are relatively shallow but widespread, extending up to 200 feet in all directions. This extensive root network helps anchor these giants securely in the rocky soils of their mountainous habitat.
Don’t Miss: Succulent Plant | Care, Types, Benefits and Décor Ideas
Facts About Giant Sequoia
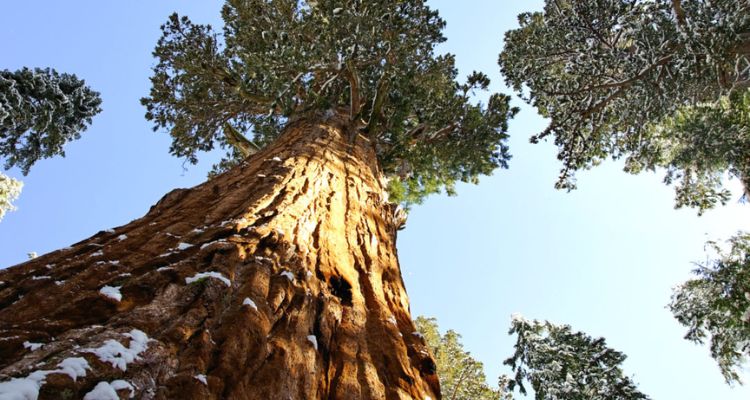

- Ancient Giants: Giant Sequoias are among the oldest living organisms on Earth. Some of these trees are over 3,000 years old, having sprouted long before the dawn of recorded history.
- Fire-Resilient: Fire is essential to the life cycle of Giant Sequoias. The heat from fires helps release seeds from their cones and clears the forest floor, providing a fertile bed for new seedlings to grow.
- Record Holders: The General Sherman tree, located in Sequoia National Park, is the largest tree by volume in the world. It stands about 275 feet tall and has a trunk volume of over 52,500 cubic feet.
- Unique Cones: The cones of Giant Sequoias can remain on the tree for up to 20 years before releasing their seeds. These seeds are tiny, about the size of a grain of oat, and rely on wind and fire to disperse.
- Limited Range: Giant Sequoias are found only in a narrow belt of the western Sierra Nevada mountains, between 5,000 and 7,000 feet in elevation.
Giant Sequoia Lifespan
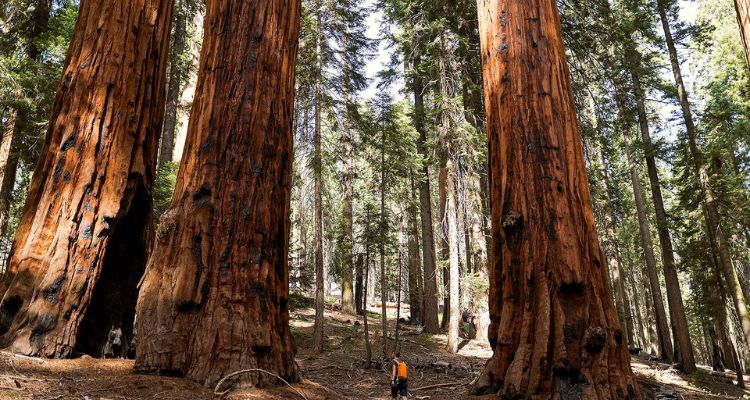

The lifespan of a Giant Sequoia is extraordinarily impressive. These trees can live for over 3,000 years, making them some of the oldest living organisms on the planet. Their longevity is attributed to several factors, including their resistance to diseases, pests, and fire, as well as their ability to regenerate new growth even after significant damage.
Giant Sequoias grow rapidly in their youth, gaining height and mass at an impressive rate. As they age, their growth slows, but they continue to expand their girth, adding new layers of wood each year. This continuous growth cycle contributes to their immense size and longevity.
Giant Sequoia Leaves
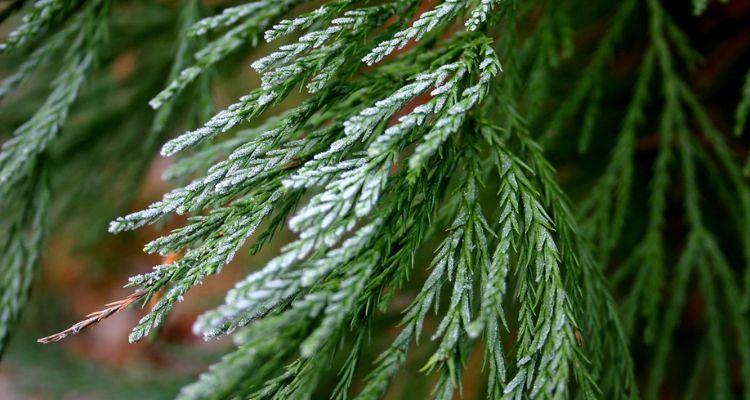

The leaves of the Giant Sequoia are scale-like and densely packed along the branches. These evergreen needles are typically blue-green and can be up to half an inch long. The leaves are adapted to conserve water, an essential trait for survival in the dry, mountainous regions where these trees grow.
The foliage of Giant Sequoias is arranged in a spiral pattern around the branches, which optimizes sunlight capture for photosynthesis. This efficient leaf arrangement, combined with their evergreen nature, allows Giant Sequoias to photosynthesize year-round, even in the harsh conditions of winter.
Don’t Miss: Sandalwood Tree | Characteristics, Uses, Facts, Lifespan, Types and More
Giant Sequoia Uses
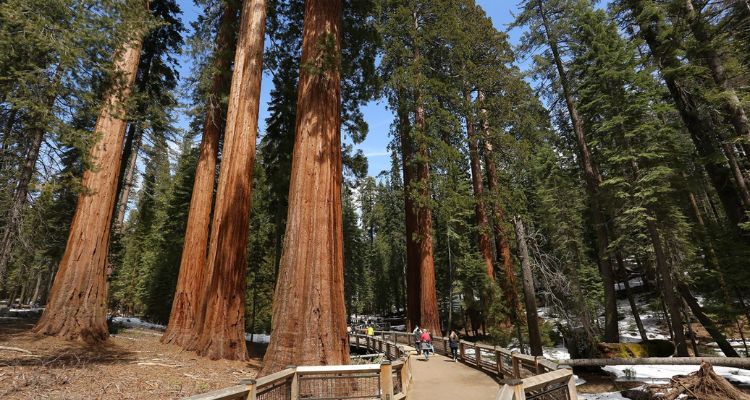

Historically, the wood of Giant Sequoias was not highly valued for commercial purposes due to its brittleness and the difficulty of transportation. However, the trees have significant ecological, cultural, and educational value.
- Ecological Importance: Giant Sequoias play a crucial role in their ecosystem. Their large canopies provide habitat for various wildlife, while their fallen logs create microhabitats for numerous plant and animal species.
- Cultural Significance: For Native American tribes, Giant Sequoias hold cultural and spiritual significance. They are often regarded as sacred and are integral to various cultural narratives and practices.
- Educational Value: Giant Sequoias serve as living laboratories for scientists studying climate change, forest ecology, and conservation biology. Their long lifespans provide valuable data on environmental changes over millennia.
- Tourism and Recreation: These majestic trees attract millions of visitors to national parks each year. The awe-inspiring sight of a Giant Sequoia can foster a deeper appreciation for nature and the importance of conservation.
Giant Sequoia Wood
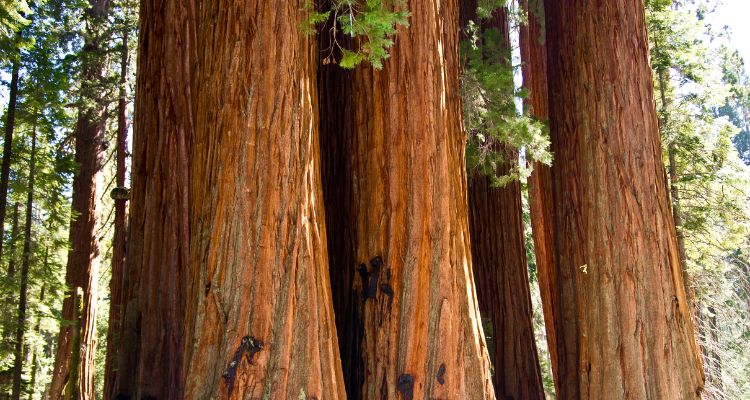

The wood of the Giant Sequoia is lightweight, relatively soft, and brittle compared to other coniferous trees. Its distinct reddish-brown color and fine grain make it visually appealing, but its tendency to splinter and break under stress limits its commercial use.
Despite these limitations, the wood of fallen Giant Sequoias has been used for various purposes, including shingles, fence posts, and novelty items. Additionally, the high tannin content of the wood makes it resistant to decay, ensuring that fallen logs can remain in the forest for centuries, continuing to provide ecological benefits long after the tree has died.
Wrapping Up
The Giant Sequoia is a testament to the wonders of nature, embodying the resilience, grandeur, and timeless beauty of the natural world. As we marvel at these ancient giants, it is crucial to recognize the importance of conserving their habitats and ensuring that future generations can continue to be inspired by their majesty. Whether you are a nature enthusiast, a casual hiker, or a dedicated conservationist, the Giant Sequoia offers a profound reminder of the enduring power of nature and our responsibility to protect it.
Don’t Miss: Fig Plant | Care, Flower, Benefits, How to Grow, Uses, and More
Some Important FAQs about Giant Sequoia Tree
What is so special about giant sequoia trees?
Giant Sequoia trees, also known as Sequoiadendron giganteum, are remarkable for several reasons. Their immense size is perhaps the most striking feature, as they are among the largest living organisms on Earth. These trees can reach heights of 250 to 300 feet, with trunk diameters exceeding 20 feet. Their thick, fire-resistant bark, which can be up to three feet thick, helps protect them from forest fires, pests, and diseases.
Moreover, Giant Sequoias are incredibly long-lived, with some individuals over 3,000 years old, making them some of the oldest living organisms on the planet. Their cones and seeds have a unique relationship with fire, as the heat from fires helps release seeds from their cones, facilitating new growth. The combination of these characteristics – size, longevity, and fire-adapted reproductive strategies – makes Giant Sequoias a fascinating and unique species in the natural world.
Where is the largest giant sequoia tree?
The largest Giant Sequoia tree, by volume, is the General Sherman tree, located in Sequoia National Park, California. The General Sherman tree stands at approximately 275 feet tall and has a trunk volume of over 52,500 cubic feet, making it the largest known living single-stem tree on the planet. The tree’s colossal size and impressive age, estimated to be between 2,300 and 2,700 years old, draw thousands of visitors each year who come to marvel at this natural wonder.
Why do giant sequoias only grow in California?
Giant Sequoias are native to a specific region in California, primarily the western slopes of the Sierra Nevada mountains, between elevations of 5,000 and 7,000 feet. This restricted range is due to the unique combination of climatic and soil conditions found in this region. The Giant Sequoias thrive in areas with deep, well-drained soils and require a specific moisture balance that is provided by the Sierra Nevada’s winter snowpack and summer thunderstorms.
The combination of mild, wet winters and dry summers creates the ideal conditions for Giant Sequoias to grow. Additionally, the region’s natural fire regime plays a crucial role in their life cycle by clearing out competing vegetation and helping to release seeds from their cones. Outside of this narrow belt, the climatic and ecological conditions are not conducive to their growth, which is why Giant Sequoias are not found naturally in other parts of the world.
Why are sequoias so rare?
Giant Sequoias are considered rare due to their limited geographic range and specific ecological requirements. They are found naturally only in about 75 groves along a narrow belt of the western Sierra Nevada mountains in California. This limited range makes them vulnerable to environmental changes and human activities that can impact their habitat.
Moreover, the ecological conditions that support their growth – specific soil types, moisture levels, and fire regimes – are not commonly found outside this region. Human activities, such as logging and land development, have also historically threatened these trees. Conservation efforts and the establishment of protected areas like national parks have been crucial in preserving the remaining Giant Sequoia groves.
What is the significance of a sequoia?
Giant Sequoias hold significant ecological, cultural, and scientific importance. Ecologically, they provide critical habitat for a variety of plant and animal species. Their large canopies offer shelter, and their fallen logs create microhabitats that support diverse forest ecosystems. Giant Sequoias also play a role in carbon sequestration, helping to mitigate climate change by storing large amounts of carbon dioxide.
Culturally, Giant Sequoias have been revered by Native American tribes and are considered symbols of longevity, resilience, and natural beauty. They attract millions of visitors each year, fostering a sense of awe and a deeper appreciation for nature.
Scientifically, Giant Sequoias offer valuable insights into forest ecology, climate change, and conservation biology. Their long lifespans provide researchers with historical data on environmental conditions over millennia, making them important subjects for studying the impacts of climate change and the effectiveness of conservation strategies.
How powerful is Sequoia?
While the term “powerful” can be subjective, Giant Sequoias exhibit several forms of “power” in their natural context. Biologically, they are powerful in their resilience and longevity. Their ability to withstand fires, pests, and diseases, combined with their immense size and long life spans, showcases their robustness and adaptability.
Ecologically, they exert a powerful influence on their environment. By dominating the canopy and contributing to the forest structure, they shape the habitat and influence the distribution of other species. Their presence impacts water cycles, soil health, and overall forest dynamics.
Culturally and symbolically, Giant Sequoias hold powerful meanings for many people. They represent endurance, strength, and the grandeur of the natural world. Their ability to inspire awe and reverence speaks to their powerful presence in human culture and consciousness.
Overall, the power of the Giant Sequoia lies in its remarkable biological characteristics, its crucial ecological roles, and its enduring significance to human culture and scientific research.
Don’t Miss: Indian Mahogany Tree | Wood, Uses, Leaf, and More